Google’s 14,000+ Ranking Factors Exposed
This year on March 13, an automated bot named yoshi-code-bot released thousands of documents from Google’s internal Content API Warehouse on Github. These documents, earlier shared with SparkToro co-founder Rand Fishkin, have been thoroughly reviewed and analyzed by Michael King, CEO of iPullRank, in an epic exposé.
I’ll be going over my interpretations of some of King’s findings and what they mean for backlink building efforts. For those interested in going over the leak themselves, it can be accessed here under the Apache 2.0 license. That means you’re able to use, modify and distribute it however you so please.
It’s important to note that what I’m going over in this article is mere interpretation, based on my experience doing SEO at scale for B2B SaaS companies. These are not facts and should not be taken as such. I also may update this article in the future; these are just my initial thoughts on a handful of ranking factors I feel are most important to link building.
Link Building Concepts Confirmed in the Google Algorithm Leak
Backlinks Matter
Despite what many SEOs claim, backlinks are still crucial for ranking, especially for competitive terms. King confirmed this by saying it directly: “Links still seem to be pretty important.” While I still subscribe to the whole content is king sentiment, there’s only so far you can go on competitive terms without actively building backlinks. I specify competitive terms here because I know firsthand how it’s possible to rank for long-tail keywords, branded terms, etc without a strong backlink profile.
Speculation: Backlinks are powerful not just because of their strong weight in ranking algorithms, but also because they are cumulative. You can stack up backlinks, but you can’t stack up meta titles for a single page.
Site Authority Exists
Contrary to what Google employees have told us, Site Authority (SA) is a real metric used in some capacity in ranking systems. Unfortunately, even after the leak, we don’t understand exactly how this metric is used.
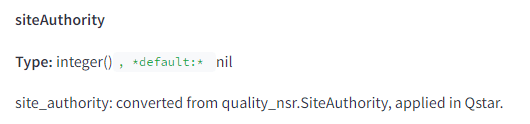
Speculation: The existence of SA confirms what we already know about DA / DR. Sites with strong, established link profiles can rank more easily. That’s why Forbes is the go-to resource for everything, from creatine to baby strollers.
Indexing Tiers
The leak revealed a metric called sourceType that explains a loose relationship between where a page is indexed in a tiered system and its value.
Google’s index organises content into tiers for efficiency. The most important content, updated regularly, is stored in flash memory for quick access. Less important information resides on solid-state drives, while content updated less frequently finds a home on standard hard drives.

What this means for off-page SEO efforts is that the higher the indexing tier, the more link equity will be passed from a link. If a page is considered “fresh” (new), it is considered higher quality and thus, a higher indexing tier.
Speculation: The most powerful links you can acquire are those from new guest blogs on high site authority domains and niche edits on pages ranking highly for contextually-relevant terms. Digital PR will continue to be a strong backlink category going forward.
Link Velocity of Spam
Google measures the velocity of spam anchor text to nullify negative SEO attacks. Spikes of spam anchor text can be detected by Google, which is why they’ve told us that disavowing spam links isn’t necessary.

What this means in practical terms is that negative SEO can still be done, but a drip-feed of consistent links that aligns with a natural-looking velocity is key. For example, if someone built 2,000 spam links to your domain, it’s unlikely that it would negatively impact your rankings on Google. However, if they drip-feed these links to your site over the course of say, a year, they could spank your website down the rankings.
Speculation: This concept could potentially be used by white hat SEOs for finding safe speed limits for building backlinks. If you took note of how fast competitors are building their backlinks, you could build backlinks at a similar rate with mitigated risk. We’ll get into this in more detail near the end of the article with a practical example using ahrefs.
Homepage Trust
Homepage backlinks print money because Google values a link based on how much the homepage is trusted.

Speculation: Backlinks from real businesses that just happen to have a blog are some of the most consistently powerful. If a blog exists purely for advertising revenue and doesn’t have a product or service offering, it’s unlikely that its homepage will be as trusted.
Links Should Stand Out
How different hyperlinks look visually compared to the rest of the text on a page is measured by Google’s ranking algorithm. This is likely how they track and punish those abusing invisible links on a page (eg. link stuffing in white text on a white background).

Speculation: Websites that don’t have anything differentiating links from regular paragraph text visually will pass less link equity than websites that do. The use of bolding, font colours and font sizes may play a role in ranking.
Anchor Text Mismatch
Websites can be hit with algorithmic demotions based on anchor text mismatches. What this means is that anchor text should have contextual relevance both ways: the anchor text should fit within a body of text contextually and the destination URL should also match what the text is about.
For example, if your anchor text was “B2B SaaS SEO”, the destination page shouldn’t be about anything other than B2B SaaS SEO.
Speculation: Anchor text matters more than we thought it did. Since mismatches can result in demotions, exact and partial keyword match anchor text is important in link building campaigns with mitigated risk.
Risk Mitigation in Backlink Building
Safe Link Velocity
Maintaining a ‘safe’ backlink velocity is especially important when going after high competition keywords where the top players are building backlinks consistently and in higher volumes. If you move too fast or use the same anchor text too much, it may be seen as spammy to Google.
In this section, I’ll be briefly going over how to estimate the pace you can build backlinks safely, according to what Google is already rewarding in the SERPs. Note that this isn’t an exact measure and should only be used as a guideline for checking competitor backlinks. Ultimately, you’ll want to build backlinks at a comfortable pace that looks similar to competitors.
Calculating Backlink Gap Between You and Competitors
This is the first piece of the puzzle when trying to figure out how many backlinks you’ll need altogether.
First, look up your keyword in your fav SEO tool. We’re going to figure out what’s needed to rank for “social media management tools” in ahrefs for this example.
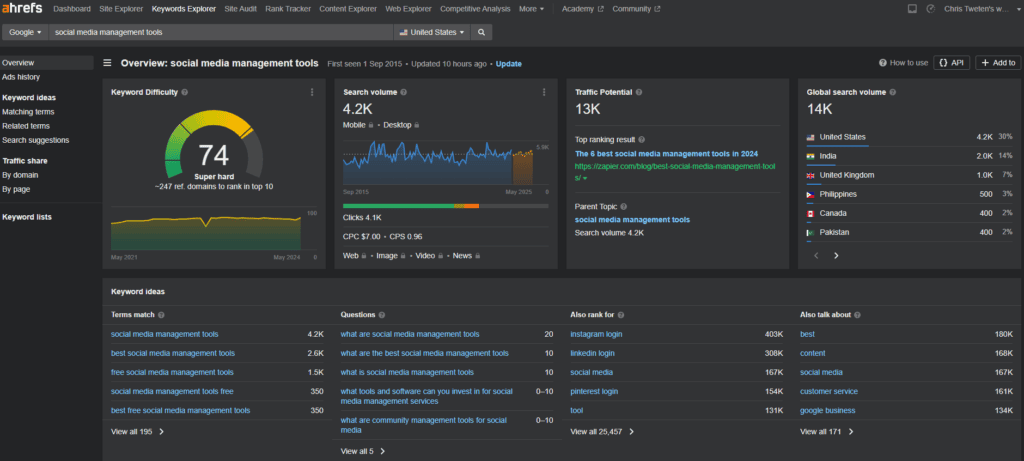
Open up the list of backlinks for each site in the top 3 of the SERP.
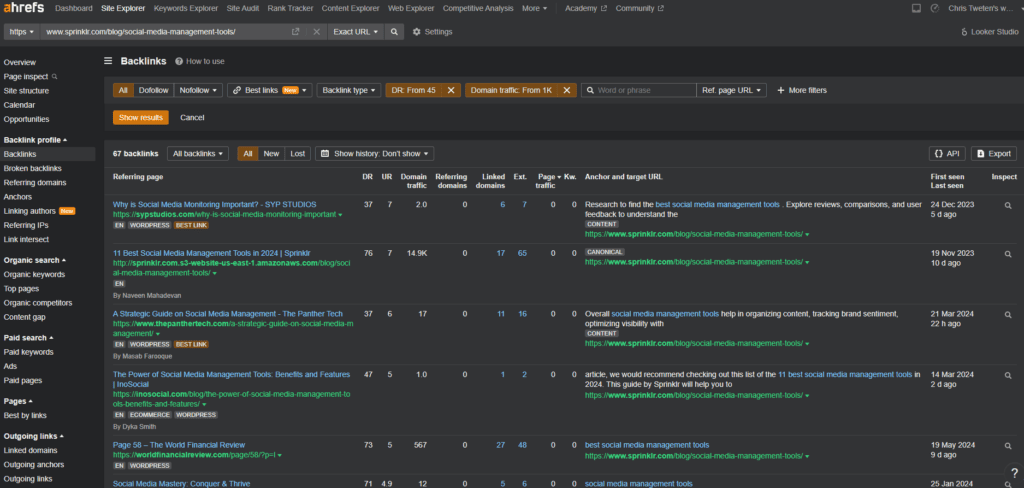
Next, apply filters that match the caliber of backlinks you build. For campaigns we run at Spacebar Collective, we guarantee dofollow links with a minimum DR of 45 and aim for a minimum monthly traffic of at least 1,000. We also want to only display one link per domain, as we’re unlikely to build multiple links from the same domain in the same campaign.
You’ll see below that the list of backlinks quickly shrinks from 67 down to only 13. ONLY 13!
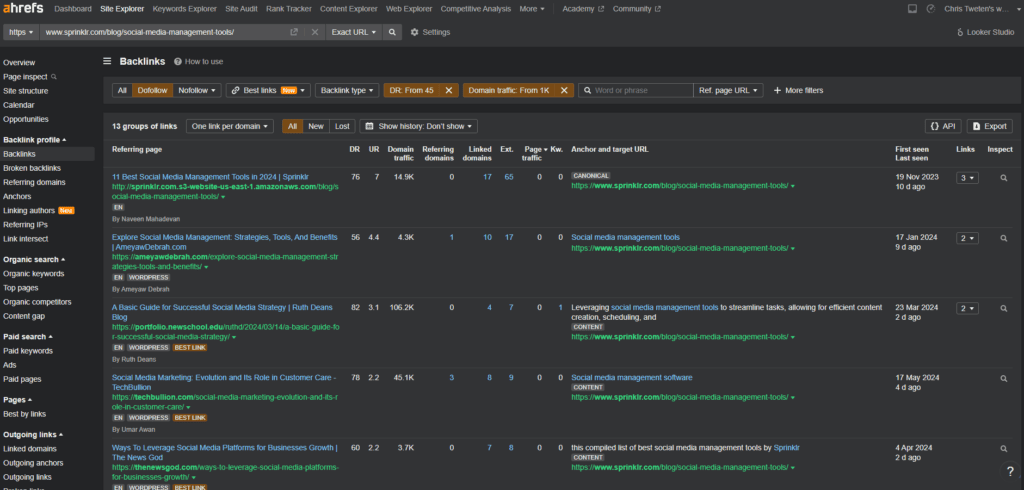
The top 3 pages in the SERP had a total 31, 13 and 85 needle-moving backlinks, respectively. From here, we average these totals, giving a rough estimate of just how many backlinks you would need to build to be on a level playing field: ~43.
This doesn’t mean it’s the exact number of backlinks you need to build to outrank them necessarily because of the many other factors at work here, but it’s a good estimate of how to match the top players.
Real Link Velocity of Competitors
Now that we know we need to build somewhere in the realm of 43 backlinks, we need to think about how quickly we want to build those backlinks. We want to do things as safely as possible, so that our links hold weight and aren’t seen as spam. 43 isn’t actually a whole lot in the grand scheme of things, so it’s unlikely we’ll look spammy (unless we built all 43 in a day or something like that).
This next step is simple: We look at how many backlinks our competitors are building on a monthly basis. You just need to tally the total number of links they’ve built up on a monthly basis over the past couple of months and go from there.
If competitors are building 10 backlinks per month, you can assume that it’s relatively safe to build at the same backlink velocity, assuming the quality and relevance of backlinks is safe and also on par with them. In the example of ranking for “social media management tools”, we want to hit the 43 backlink total count, so at that pace, it’d take a little over 4 months to hit our target.
Common Criteria for Domains You Build Links From
Minimum DR / DA
Yes, these domain-level metrics are from 3rd party tools and aren’t used directly by Google when ranking pages.
But…
Google has its own metric that it does use in some capacity: Site Authority (SA).
Backlinks from sites with stronger backlink profiles give more link equity, meaning you need fewer backlinks to rank than if building backlinks from lower SA domains. While it’s not a good metric on its own, it can be powerful when combined with other criteria.
Minimum Traffic Requirements
Websites and pages that bring in search traffic are weighted more heavily than those that don’t. I think it’s safe to say that pages that are earning lots of traffic and passing on lots of referral traffic give out more link equity than those that do not.
Contextual Relevance
Contextual relevance is an important one to consider when building backlinks. You’ll want to make sure that there is contextual relevance from a domain-level as well as at a page-level. The anchor text you select should also match the destination URL and the anchor text should make sense contextually within the body of text on the page it’s on.
tl;dr
Backlinks matter just as much as they ever have and the Google algorithm leak confirmed a lot of speculations we’ve had over the years. Hope this guide helps guide your backlink building efforts. If you have any questions, input or disagreements, feel free to drop a comment or hit me up on X @ctwtn.